PRIN2022 - G4-APTASTAT - Design, synthesis and investigations on new G-quadruplex aptamers against STAT3 and the interleukine-6 receptor
Titolo progetto: PRIN2022 - G4-APTASTAT - Design, synthesis and investigations on new G-quadruplex aptamers against STAT3 and the interleukine-6 receptor
Programma di finanziamento: PRIN 2022
Responsabile scientifico: prof.ssa Valentina Rapozzi
Ruolo del DAME: partner
Descrizione generale:
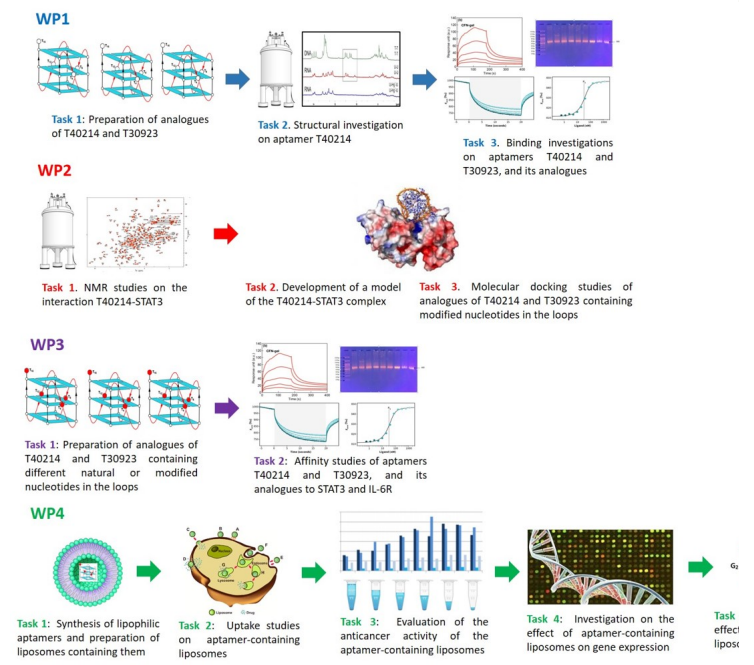
STAT3 is a factor activated in response to the binding of a number of ligands, as cytokines (e.g. IL-6) and other factors, to their cognate cell surface receptors (e.g. IL-6R). This protein has been identified as an important target for cancer therapy, since it participates in oncogenesis through the upregulation of genes encoding apoptosis inhibitors (Bcl-xL, Mcl-1 and survivin), cell-cycle regulators (cyclin D1 and c-myc), and inducers of angiogenesis. Growing evidences have shown that STAT3 is also constitutively activated in many human cancers, highlighting the prognostic significance of its levels in invasive breast cancer and chordomas. Therefore, targeting this protein through ligands with high affinity and specificity has both therapeutic and diagnostic potential. T40214 is G-quadruplex (G4) aptamer [(G3C)4] able to link STAT3 in an efficient manner in several cancer cell lines and tumor xenografts. However, T40214 requires the formation of a complex with polyethylenimine to be efficiently delivered in cells and protected against degradation. Moreover, the folding kinetic for the formation of the active and nuclease resistant G4 conformation is quite slow, considering the extracellular low K+ concentration. The design and implementation of appropriate modifications to enhance the general properties of T40214 requires detailed information concerning both the active conformation of the aptamer and its interaction with the target protein. Although an antiparallel G4 conformation has been proposed for T40214, this structure has been severely questioned by recent investigations showing that T40214 adopts a parallel G4 conformation. These considerations require an in depth revision of the investigations concerning the T40214/STAT3 complex, since binding studies regarding their interaction in isolated systems are completely lacking. Another aptamer related to T40214 and targeting STAT3, namely T40231 [G2T(G3T)2G3], has also shown similar biological properties as T40214. Interestingly, another G4 aptamer with a sequence similar to T40231, namely T30923 [(G3T)4], has been proven to bind to IL-6R which in turn activates STAT3. Considering that T40214 and T30923 adopt similar parallel G4 structures, these data give us the unique opportunity to design and prepare an aptamer targeting both proteins, IL-6R and STAT3, involved in the same bio-molecular pathway. The main aims of this project are: 1) preparing and studying T40214 analogues with improved general stability properties; 2) investigating the interaction between T40214, its analogues and STAT3; 3) preparing and studying modified aptamers able to efficiently bind to both STAT3 and IL-6R; 4) exploring the possibility to engraft the designed aptamers into POPC liposomes in order to improve their delivery into cancer cells; 5) evaluating the biological activity of the most promising aptamers against pancreatic cancer adenocarcinoma cells and other cancer cell lines.
Partner del progetto:
- Università degli Studi di Napoli Federico II
- Università degli Studi di Milano
- Università degli Studi di Udine
Date inizio e fine progetto: 05.10.2023 – 04.10.2025
Budget totale del progetto: 103.692,00€
Sito web: prin.mur.gov.it
Finanziato dall’Unione europea – Next Generation EU